Dra. Isabel Rozas
Dra. Isabel Rozas, Full Professor at the School of Chemistry of the Trinity College (Dublin)
A dónde puede llevarte elegir el ADN como diana biológica
Room 0.6, Edificio Polivalente, UAH. January 11st, 16.00.
On-line: Rozas talk

Dra. Isabel Rozas, Full Professor at the School of Chemistry of the Trinity College (Dublin)
A dónde puede llevarte elegir el ADN como diana biológica
Room 0.6, Edificio Polivalente, UAH. January 11st, 16.00.
On-line: Rozas talk

Last Tuesday, December 12, Dr. Javier Carreras successfully passed hir exam and was appointed as Associate Professor at the UAH.
Congratulations Javi!

Ana Milián, Lucía Sánchez-Jiménez, Jaime Tostado, Juan J. Vaquero, Manuel A. Fernández-Rodríguez*, Patricia García-García*
Adv. Synth. Catal. 2023, Accepted Articles
DOI: 10.1002/adsc.202301136
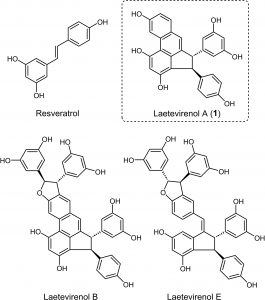
| The total synthesis of Laetevirenol A, a natural product with antioxidant activity, has been achieved. A gold-catalyzed cycloisomerization of an o-alkenyl-o’-alkynylbiphenyl has been used as the key step for the construction of the phenanthrene moiety present in Laetevirenol A. Several studies in model substrates have been carried out to unveil the effect of substituents in different locations in the outcome of this cyclization, which allowed the design of an appropriate precursor for the fundamental gold-catalyzed cycloisomerization. The suitably functionalized phenanthrene intermediate obtained in this key step could be further transformed into Laetevirenol A via a Friedel-Crafts cyclization, which also turned out to be dependent on the nature of the substituents. Finally, Laetevirenol A was obtained in 10 steps from commercially available substrates, with a 20% global yield. |
Dr. Patricia García has received the award for junior director in the area of science, health sciences, engineering and architecture in the 2023 call.
This award is a recognition of the work done by the faculty of the University of Alcalá for obtaining results in the field of research training.
Congratulations!
Francisco Maqueda-Zelaya, José Luis Aceña*, Estíbaliz Merino, Juan J. Vaquero, and David Sucunza*
J. Org. Chem. 2023, ASAP
DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.3c01675
| An efficient methodology to form 4-alkoxy- and 4-aryloxybenzo[d][1,2,3]triazines via an intramolecular heterocyclization of 1-azido-2-[isocyano(p-tosyl)methyl]benzenes under basic conditions has been developed. DFT calculations have been performed to further understand the mechanism of this heterocyclization, which occurs in good to excellent yields with a broad scope. |
Alcalá de Henares, 4 – 8 septembre
– Póster:
· Copper-catalyzed intramolecular cyclization of alkynylazobenzenes for the synthesis of 2H-indazoles
Clara Mañas, Juan Herrero, Estíbaliz Merino
– Póster:
· Visible-Light-Mediated Regioselective Chlorosulfonylation of Acrylamides
Guillermo G. Otárola, Mercedes Zurro, Sergio Torres-Oya, Juan José Vaquero, Estíbaliz Merino
– Póster:
· Direct conversion of C1−C6 alkanes into trifluoromethyl derivatives
Jonathan Martínez-Laguna, M. Ángeles Fuentes, Julia Altarejos, Javier Carreras, Ana Caballero, Pedro J. Pérez
Mercedes Zurro, Sergio Torres-Oya, Estíbaliz Merino*
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2023, Accepted Articles
DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.202300535
| Synthesis of anticancer drug bicalutamide promoted by visible light in one step from the corresponding N-arylacrylamide is described. This approach involves a one-pot hydroxysulfonylation reaction via a photocatalytic redox process. The use of Na2Eosin Y as photocatalyst and blue light allows the access to a broad range of α-hydroxysulfonylamides bearing a quaternary center in moderate to good yields with complete regioselectivity via radical process. |
Julia Altarejos, Estíbaliz Merino, David Sucunza, Juan J. Vaquero, and Javier Carreras*
J. Org. Chem. 2023, ASAP
DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.3c00396
| A facile access to 5-aryl-3-trifluoromethylpyrazoles has been developed by a one-pot (3 + 2) cycloaddition–isomerization–oxidation sequence employing 2,2,2-trifluorodiazoethane and styryl derivatives. A broad variety of functional groups and good yields are achieved under mild conditions. Additionally, the functionalization of 3-trifluoromethylpyrazoles was studied. DFT calculations of the cycloaddition transition state energies are consistent with the experimentally observed reactivity. |
The University of Alcalá has recognized with the Silver Medal the outstanding professional career of Professor Dr. Juan José Vaquero. Congratulations!

Professor Dr. Juan José Vaquero will become Professor Emeritus in September, after a long and successful career at the UAH.
His group organized a tribute to him together with colleagues, former collaborators and friends.