23rd Tetrahedron Symposium
Gothenburg, Sweden, 27 – 30 junio
– Póster:
· Visible light as a single reagent to promote new transformations in azobenzenes
Clara Mañas, Estíbaliz Merino
– Póster:
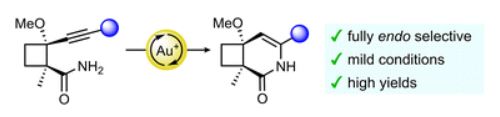
· Synthesis of 5-aryl-3-trifluoromethylpyrazoles: one-pot [3+2] cycloaddition-isomerization-oxidation
Julia Altarejos, Estíbaliz Merino, David Sucunza, Juan José Vaquero, Javier Carreras
– Póster:
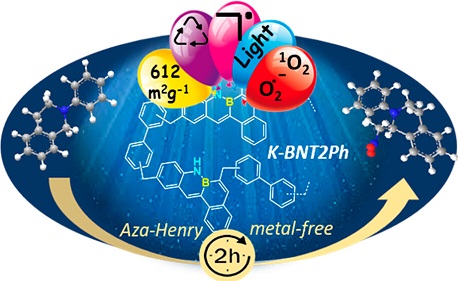
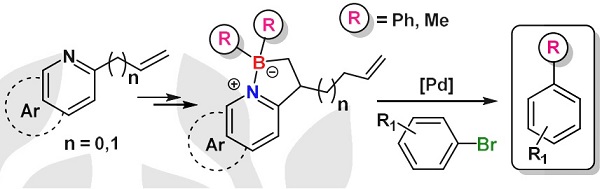
· Synthesis of borylated polycycles by metal-free borylative cyclization of enynes
Ana Milián, Ester Sans-Panadés, Marcos Humanes, Cintia Virumbrales, Estíbaliz Merino, Roberto Sanz, Juan J. Vaquero, Manuel A. Fernández-Rodríguez, Patricia García-García
– Póster:
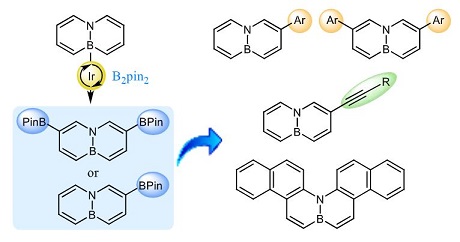
· Ir-Catalyzed C−H Borylation of 4a,8a-Dihydro-4a-Aza-8a-Boranaphthalene
Isabel Valencia, Patricia Garcia-Garcia, David Sucunza, Francisco Mendicuti, Juan J. Vaquero
XXXIX Reunión Bienal de la RSEQ
Zaragoza, 27 – 30 junio
– Póster:
· Visible Light Na2Eosin Y Catalysed Hydroxysulfonylation of Acrylamides. Straightforward Access to Anticancer Drug Bicalutamide
Mercedes Zurro, Sergio Torres-Oya, Estibaliz Merino*
– Póster/Flash:
· BF3-promoted cascade cyclization of biaryl embedded 1,8-enynes
Jaime Tostado, Juan J. Vaquero, Manuel A. Rodríguez
– Póster:
· Synthesis of benzo[1.2.3]triazines by heterocyclization of TOSMIC derivatives
Francisco Maqueda, David Sucunza, José Luis Aceña, Juan José Vaquero
– Póster/Flash:
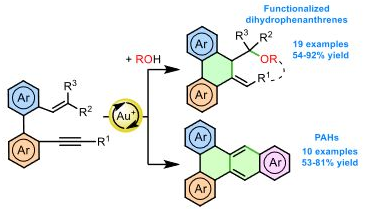
· Synthesis of polycyclic hydrocarbons by gold-catalyzes tandem formation of 4-, 5- and 7-membered rings
L. Sánchez-Jiménez, A. Gargantiel, P. García-García, M. A. Fernández-Rodríguez
– Póster/Flash:
· Towards new peptide-based compounds: synthesis of a series of novel bicyclic amino acids
Álvaro González-Molina, José Luis Aceña y Juan José Vaquero
– Póster/Flash:
· New photoreactivity of azobenzenes towards complex N-heterocycles
Clara Mañas, Estíbaliz Merino
IX Symposium of Medicinal Chemistry Young Researchers
Santiago de Compostela, 22 junio
· Novel bicyclic amino acids as potential building blocks for new peptidomimetics
Álvaro González-Molina, José Luis Aceña y Juan José Vaquero