Pyridazino-pyrrolo-quinoxalinium salts as highly potent and selective leishmanicidal agents targeting trypanothione reductase
Héctor de Lucio, Javier García-Marín, Patricia Sánchez-Alonso, Juan Carlos García-Soriano, Miguel Ángel Toro, Juan J Vaquero, Federico Gago, Ramón Alajarín, Antonio Jiménez-Ruiz
Eur. J. Med. Chem. , 2021
DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113915
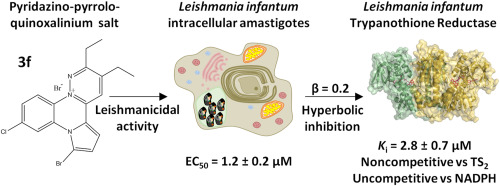
| Fifteen pyridazino-pyrrolo-quinoxalinium salts were synthesized and tested for their antiprotozoal activity against Leishmania infantum amastigotes. Eleven of them turned out to be leishmanicidal, with EC(50) values in the nanomolar range, and displayed low toxicity against the human THP-1 cell line. Selectivity indices for these compounds range from 10 to more than 1000. Compounds 3b and 3f behave as potent inhibitors of the oxidoreductase activity of the essential enzyme trypanothione disulfide reductase (TryR). Interestingly, binding of 3f is not affected by high trypanothione concentrations, as revealed by the noncompetitive pattern of inhibition observed when tested in the presence of increasing concentrations of this substrate. Furthermore, when analyzed at varying NADPH concentrations, the characteristic pattern of hyperbolic uncompetitive inhibition supports the view that binding of NADPH to TryR is a prerequisite for inhibitor-protein association. Similar to other TryR uncompetitive inhibitors for NADPH, 3f is responsible for TryR-dependent reduction of cytochrome c in a reaction that is typically inhibited by superoxide dismutase. |